Product
Ultrasonic Motor (Piezo Sonic Motor)
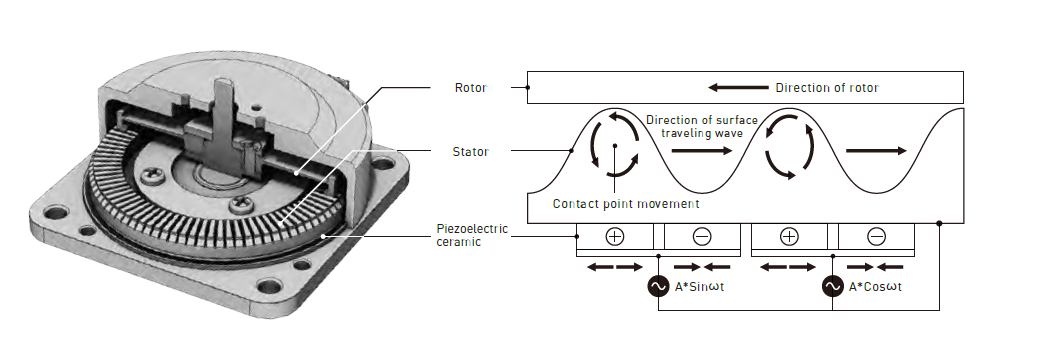
Instead of using coils or magnets to generate rotational energy, we use piezoelectric ceramics that deform when a voltage is applied.
The amount of deformation of the piezoelectric ceramic is amplified by a metal part called the stator, and by controlling the deformation, rotational motion is generated on the surface of the stator.
This rotational movement is transmitted by frictional force to the rotor pressing against the stator, and the rotor rotates. The shaft is fixed to this rotor and transmits the torque and rotation of the motor to the outside.
Since this frictional force is constantly generated, it can maintain its position even when it is not energized or controlled (high holding force), and it is possible to realize a direct drive without backlash.
Conventional ultrasonic motors have higher torque than motors that rotate with electromagnetic force of the same size (DC motors, etc.), but the problem is that their lifespan is as short as about 1/10.
By reviewing the structure and materials of the Piezo Sonic ultrasonic motor, we have succeeded in extending the life of the ultrasonic motor by more than twice that of the conventional ultrasonic motor of the same size.
In addition, a significant increase in torque has also been achieved.
We are providing Ultrasonic Motors to be used for General Envionment and Magnetic Field Environment.
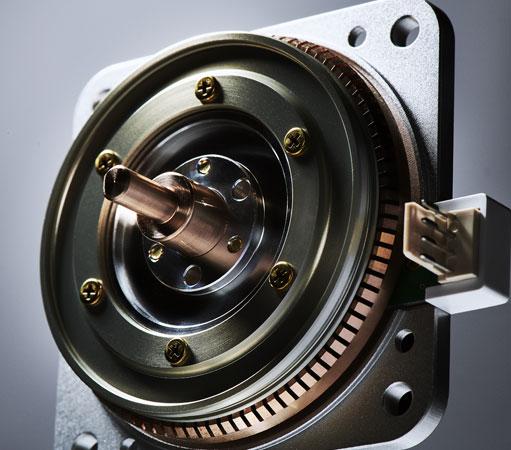
For General Field |
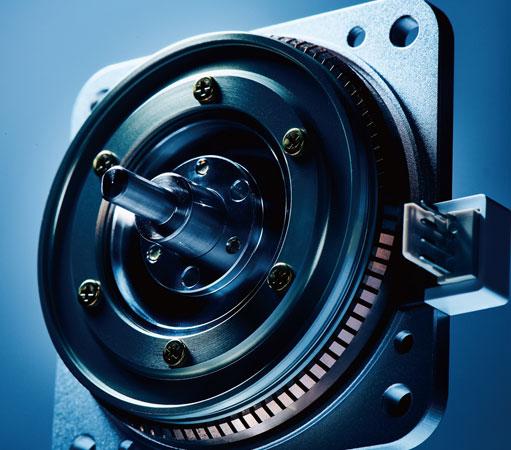
For Magnetic Field |
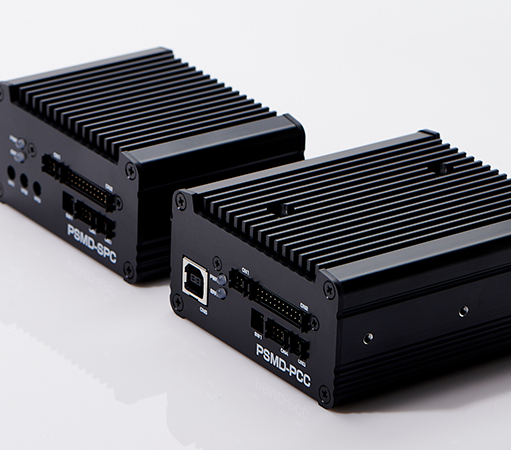
Driver |
 |
 |
 |
| PSM60S-( ) | PSM60N-( ) | Driver |
| PSM40S-( ) | PSM40N-( ) |
Movie for advantage of Pizo Sonic Motor⇓
Piezo Sonic 2 introduction-of-motor-business-of-piezo-sonic-corporation from Messe Düsseldorf on Vimeo.
⇐ Back to Ultrasonic Motor

